Are the categories by which data are grouped. – Data categorization is the process of organizing data into meaningful groups based on shared characteristics. It plays a crucial role in data management, enabling efficient storage, retrieval, analysis, and decision-making. This article delves into the purpose, benefits, types, methods, management, and applications of data categorization, providing a comprehensive understanding of this fundamental data management practice.
Data categorization involves identifying common attributes or properties within a dataset and grouping similar data points together. This process facilitates data organization, making it easier to locate and retrieve specific information when needed.
1. Data Categorization
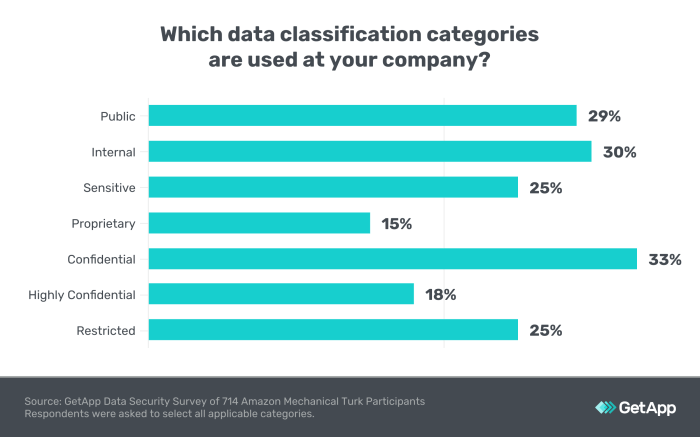
Data categorization is the process of organizing data into groups based on shared characteristics. It involves assigning labels or categories to data points, making it easier to manage, analyze, and retrieve information.
Categorizing data offers numerous benefits, including improved data organization, enhanced data analysis, efficient data retrieval, and better decision-making.
Examples of how data is grouped into categories include:
- Customer data: categorized by demographics, purchase history, and location
- Product data: categorized by type, size, color, and price
- Sales data: categorized by region, product, and time period
2. Types of Data Categories
Nominal Categories, Are the categories by which data are grouped.
Nominal categories are used to group data points that have no inherent order or ranking. The categories are simply labels used to differentiate between data points.
Examples:
- Gender (male, female, other)
- Marital status (single, married, divorced)
- Job title (manager, engineer, accountant)
Ordinal Categories
Ordinal categories are used to group data points that have a natural order or ranking. The categories are ordered from lowest to highest or vice versa.
Examples:
- Education level (high school, college, graduate school)
- Customer satisfaction (very dissatisfied, dissatisfied, neutral, satisfied, very satisfied)
- Movie rating (1 star, 2 stars, 3 stars, 4 stars, 5 stars)
Interval Categories
Interval categories are used to group data points that have a consistent interval between them. However, the zero point is arbitrary and does not represent a true absence of the measured quantity.
Examples:
- Temperature (in degrees Fahrenheit or Celsius)
- Time (in hours, minutes, or seconds)
- Weight (in pounds or kilograms)
Ratio Categories
Ratio categories are used to group data points that have a true zero point. The ratio between any two data points is meaningful.
Examples:
- Height (in inches or centimeters)
- Income (in dollars or euros)
- Population (in number of people)
3. Methods for Categorizing Data
Manual Methods
Manual methods involve manually assigning categories to data points based on predefined rules or criteria.
Advantages:
- High level of control over the categorization process
- Suitable for small datasets
Disadvantages:
- Time-consuming and labor-intensive
- Prone to human error and bias
Automated Methods
Automated methods use algorithms and machine learning techniques to categorize data points based on predefined rules or statistical models.
Advantages:
- Fast and efficient
- Can handle large datasets
- Reduces human error and bias
Disadvantages:
- May require extensive data preparation
- Can be less accurate than manual methods for complex data
4. Data Category Management
Effective data category management is crucial for maintaining the integrity and consistency of data categorization.
Best practices include:
- Establishing clear and consistent categorization rules
- Using a data dictionary or taxonomy to define categories
- Regularly reviewing and updating categories as needed
- Implementing data governance processes to ensure compliance with categorization standards
5. Applications of Data Categorization
Data categorization is widely used across various industries and applications:
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM):Categorizing customers based on demographics, behavior, and preferences
- Healthcare:Categorizing patients based on diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis
- Finance:Categorizing financial transactions based on type, amount, and date
- Market Research:Categorizing survey responses based on demographics, opinions, and preferences
- Data Analysis:Categorizing data to identify patterns, trends, and insights
6. Challenges in Data Categorization: Are The Categories By Which Data Are Grouped.
Common challenges include:
- Data inconsistency:Data points may have conflicting or missing values, making categorization difficult
- Subjectivity:Categorization can be subjective, leading to inconsistent results
- Evolving data:Data can change over time, requiring categories to be updated or revised
Overcoming these challenges involves:
- Implementing data quality checks to ensure data consistency
- Establishing clear categorization guidelines to minimize subjectivity
- Regularly reviewing and updating categories to keep pace with evolving data
Common Queries
What is the primary purpose of data categorization?
The primary purpose of data categorization is to organize data into meaningful groups based on shared characteristics, facilitating efficient data storage, retrieval, and analysis.
What are the key benefits of data categorization?
Data categorization offers several key benefits, including improved data organization, easier data retrieval, enhanced data analysis, and better decision-making.