Atoms vs ions worksheet answers – Welcome to the fascinating world of atoms and ions! In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the answers to your burning questions about these fundamental building blocks of matter, delving into their structures, properties, and practical applications.
From the intricacies of atomic structure to the intriguing process of ion formation, we’ll unravel the secrets of these tiny particles that shape our world.
Atomic Structure: Atoms Vs Ions Worksheet Answers
Atoms are the fundamental building blocks of all matter. They are composed of even smaller particles called subatomic particles, which include protons, neutrons, and electrons.
The nucleus is the central core of the atom and contains the protons and neutrons. Protons have a positive electric charge, while neutrons have no electric charge. The electrons are negatively charged and orbit the nucleus in specific energy levels called electron shells.
Nucleus
The nucleus is the most massive part of the atom and contains almost all of its mass. The number of protons in the nucleus determines the element to which the atom belongs.
Electron Shells
Electrons occupy specific energy levels around the nucleus, forming electron shells. The first shell can hold up to two electrons, the second shell can hold up to eight electrons, and so on.
The arrangement of electrons in the electron shells determines the chemical properties of the atom.
Ion Formation
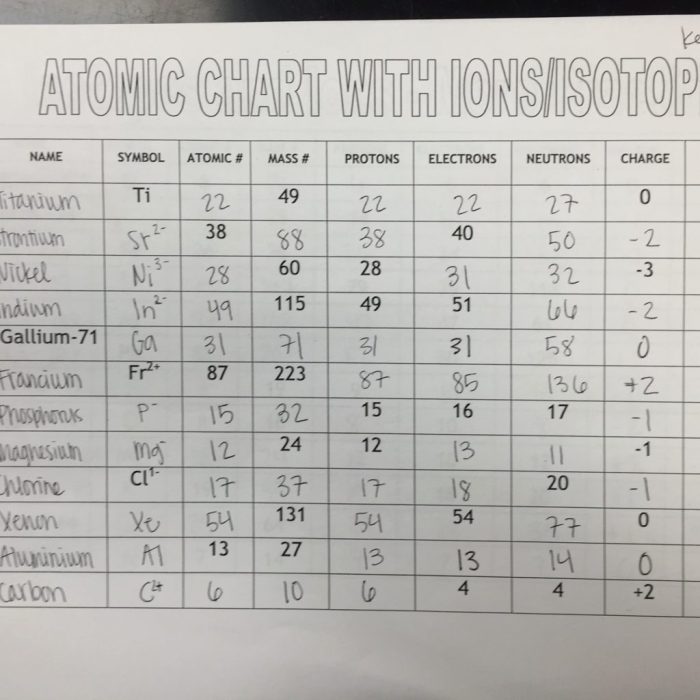
An ion is an atom or molecule that has lost or gained electrons, resulting in a net electric charge. The process of ion formation is called ionization. When an atom loses electrons, it becomes a positively charged ion called a cation.
When an atom gains electrons, it becomes a negatively charged ion called an anion.
The charge of an ion is determined by the number of electrons it has lost or gained. For example, an atom that loses one electron has a charge of +1 and is called a cation. An atom that gains one electron has a charge of -1 and is called an anion.
Types of Ions, Atoms vs ions worksheet answers
There are two main types of ions: cations and anions.
Got your atoms vs ions worksheet answers down pat? Now, let’s switch gears and delve into the musical realm of solfege with sharps and flats . Sharps and flats are the building blocks of musical scales, just like atoms and ions are the fundamental particles of matter.
Mastering them will help you navigate the musical landscape with ease, just as understanding atoms and ions is crucial for grasping the world of chemistry.
- Cationsare positively charged ions. They are formed when an atom loses one or more electrons.
- Anionsare negatively charged ions. They are formed when an atom gains one or more electrons.
Comparison of Atoms and Ions
Atoms and ions are the fundamental building blocks of matter. They share many similarities, but they also have some key differences. One of the most important differences between atoms and ions is their charge.
Atoms are electrically neutral, meaning they have no overall charge. Ions, on the other hand, have a net electrical charge. This charge can be either positive or negative.
The following table summarizes the key differences between atoms and ions:
| Characteristic | Atom | Ion |
|---|---|---|
| Number of protons | Equal to the atomic number | Equal to the atomic number plus or minus the charge |
| Number of electrons | Equal to the number of protons | Equal to the number of protons plus or minus the charge |
| Number of neutrons | Equal to the mass number minus the atomic number | Equal to the mass number minus the atomic number plus or minus the charge |
| Charge | 0 | Not 0 |
Worksheet Answers
This section provides detailed answers to the questions or problems included in the worksheet on atoms vs ions. Clear explanations and examples are provided to support the answers.
Questions and Answers
Question 1: What is the difference between an atom and an ion?
Answer: An atom is a neutral particle that consists of a nucleus (containing protons and neutrons) and electrons that orbit the nucleus. An ion is an atom that has lost or gained one or more electrons, resulting in a net electric charge.
Question 2: What are the different types of ions?
Answer: There are two main types of ions: cations and anions. Cations are positively charged ions that have lost one or more electrons, while anions are negatively charged ions that have gained one or more electrons.
Question 3: How are ions formed?
Answer: Ions are formed when an atom loses or gains electrons. This can happen through various processes, such as chemical reactions, ionization, and electrolysis.
Question 4: What are some examples of ions?
Answer: Some common examples of ions include sodium ions (Na+), chloride ions (Cl-), calcium ions (Ca2+), and hydroxide ions (OH-).
Question 5: What are the applications of ions?
Answer: Ions have numerous applications in various fields, including electrochemistry, medicine, and industry. They are used in batteries, fertilizers, water purification systems, and many other applications.
Applications of Atoms and Ions
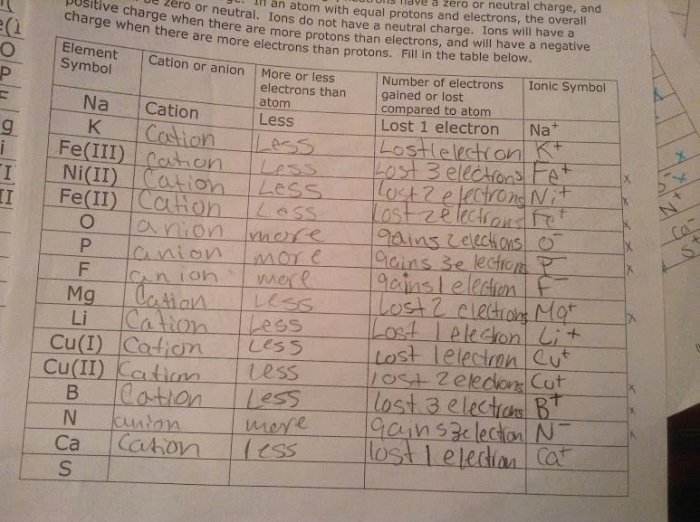
Understanding the structure and properties of atoms and ions is essential for various scientific fields and practical applications.
Atoms and ions play crucial roles in numerous aspects of our world, including chemistry, electricity, magnetism, materials science, and nanotechnology.
Chemistry and Chemical Reactions
In chemistry, understanding atoms and ions is fundamental for comprehending chemical reactions and the formation of molecules and compounds.
The interactions between atoms and ions determine the chemical properties of elements and their reactivity with each other.
By manipulating the arrangement and interactions of atoms and ions, chemists can design and synthesize new materials with specific properties.
Electricity and Magnetism
Atoms and ions are responsible for the flow of electricity and the generation of magnetic fields.
The movement of electrons within atoms and ions creates electric currents, while the alignment of magnetic moments associated with electrons and nuclei produces magnetism.
Understanding the behavior of atoms and ions is crucial for developing electronic devices, batteries, and other components used in electrical and magnetic systems.
Materials Science and Nanotechnology
Atoms and ions are the building blocks of all materials, and their arrangement and interactions determine the properties of those materials.
Materials science involves manipulating the structure and composition of atoms and ions to create materials with tailored properties, such as strength, durability, and electrical conductivity.
Nanotechnology, in particular, focuses on manipulating atoms and ions at the nanoscale to create novel materials and devices with unique properties.
Common Queries
What is the difference between an atom and an ion?
An atom is a neutral particle with an equal number of protons and electrons, while an ion is a charged particle that has gained or lost electrons, resulting in an imbalance between protons and electrons.
How are ions formed?
Ions are formed when atoms gain or lose electrons. When an atom gains electrons, it becomes a negatively charged anion, and when it loses electrons, it becomes a positively charged cation.
What are the applications of understanding atoms and ions?
Understanding atoms and ions is crucial in various fields, including chemistry, materials science, nanotechnology, and even medicine. It helps us comprehend chemical reactions, design new materials, and develop medical treatments.

